fingerprint
https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/fingerprint-scanner-gt-521fxx-hookup-guide
The image below shows the fingerprint scanner’s optical sensing area where the device will be able to scan your fingerprint.
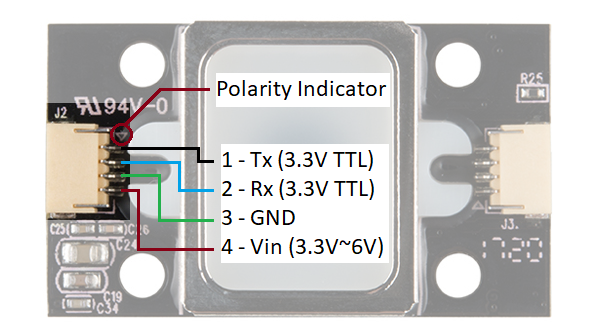
There is a marking next to the JST-SH connector that indicates polarity. The JST-SH connector breaks out the pins for serial UART and power. While the input voltage is between 3.3V and 6V, the UART’s logic level is only 3.3V. You will need a logic level converter or voltage divider to safely communicate with a 5V device.
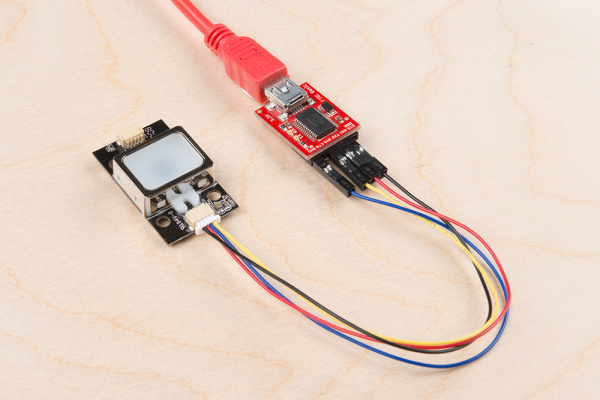
After connecting, the setup should look like the image below.
For more information on how to make a custom adapter, please refer to the older tutorial. Remember, the pin locations are the same so the adapter can work with the current fingerprint scanner.
Hardware Overview
Features
The GT-521F32 and GT-521F52 have a lot in common with the previous models. They have the same protocol commands and packet structure. Code that was implemented for previous models should be functionally the same. The fingerprint scanner has the ability to:- Enroll a Fingerprint
- Identify a Fingerprint
- Capable of 360° Recognition
- Different Board Layout
- 4x Mounting Holes
- 2x JST SH Connectors
- Touch Interface
| Technical Specs | GT-521F32 / GT-521F52 |
|---|---|
| CPU | ARM Cortex M3 Cortex |
| Sensor | optical |
| Window | 16.9mm x 12.9mm |
| Effective Area of the Sensor | 14mm x 12.5mm |
| Image Size | 258x202 Pixels |
| Resolution | 450 dpi |
| Max # of Fingerprints | 200 / 3000 |
| Matching Mode | 1:1, 1:N |
| Size of Template | 496 Bytes(template) + 2 Bytes (checksum) |
| Serial Communication | UART (Default: 9600 baud) and USB v2.0 (Full Speed) |
| False Acceptance Rate (FAR) | < 0.001% |
| False Rejection Rate (FRR) | < 0.01% |
| Enrollment Time | < 3 sec (3 fingerprints) |
| Identification Time | <1.5 |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V ~ 6Vdc |
| Operating Current | < 130mA |
| Touch Operating Voltage | 3.3Vdc |
| Touch Operating Current | < 3mA |
| Touch Standby Current | < μ5 |
There is a marking next to the JST-SH connector that indicates polarity. The JST-SH connector breaks out the pins for serial UART and power. While the input voltage is between 3.3V and 6V, the UART’s logic level is only 3.3V. You will need a logic level converter or voltage divider to safely communicate with a 5V device.
Note: Make sure that you are connecting to the correct JST
connector indicated by the polarity marker and capacitors. The JST
connector on the other side of the board are not connected to the same
pins for serial UART.
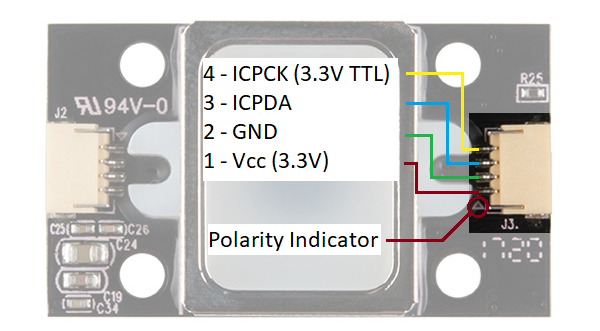
The GT-521F32 and GT-521F52 have the ability to sense if a finger is
placed on the optical sensing area. Upon contact with the metal frame
around the optical sensing area, the ICPCK will output 3.3V (HIGH).
Otherwise, the ICPCK will be 0V (LOW)| Touch State | ICPCK Pin Status |
|---|---|
| Finger Initially Touching the Frame | LOW => HIGH |
| No Finger Touching | LOW => LOW |
| Finger Touching the Frame | HIGH => HIGH |
| Removing a Finger From the Frame | HIGH => LOW |
Note: If the fingerprint scanner is powered from the UART side, you will need to still provide 3.3V to power the touch interface. The GND is connected to GND plane.
Hardware Hookup
The fingerprint scanner requires a serial UART connection and power. There are a few options to connect to the sensor depending on what UART device you are using. The easiest would be to use an FTDI but you can also use any microcontroller that has a UART.1.) Connecting w/ a 3.3V FTDI
Option 1: Qwiic Cable
To connect the fingerprint scanner to your computer, it is recommended to connect the JST SH cable to a USB-to-serial converter. Here are the minimum required parts you would need to get started:- Fingerprint Scanner (GT-521F32 or GT-521F52)
- Qwiic Cable - Breadboard Compatible
- 3.3V FTDI Basic Breakout
- Mini-B USB Cable
| Fingerprint Scanner [Pin #] | FTDI 3.3V |
|---|---|
| UART_TX (3.3V TTL) [Pin 1] | RX |
| UART_RX (3.3V TTL) [Pin 2] | TX |
| GND [Pin 3] | GND |
| Vin (3.3V~6V) [Pin 4] | 3.3V |
Note: The colors of the Qwiic Cable are standard for I2C
connections, not UART, so the colors will not match typical standards
for colored cables. For example, the red wire in this circuit connects
Rx to Tx. Double check your connections before powering the scanner.
Option 2: Making a Custom Adapter
If you are using the JST SH Jumper 4 Wire Assembly instead of the Qwiic cable, it is highly recommended that you make a custom adapter by soldering to the ends of the wire for a secure connection. This will ensure that the connection is not loose when inserting it into female header sockets of an FTDI or the RedBoard/Arduino Uno. The cable wire is small compared to the female header socket. A small bump can mess with the serial UART or power between the fingerprint scanner and converter. This may require you to reconnect the scanner to your computer or device. Making an adapter will also provide quick access to the small 4-pin JST-SH connector that is on the scanner.For more information on how to make a custom adapter, please refer to the older tutorial. Remember, the pin locations are the same so the adapter can work with the current fingerprint scanner.
Comentarios
Publicar un comentario